Have you ever wondered what makes Bitcoin and other digital currencies so secure? Or why people say blockchain technology could change everything from banking to healthcare?
Understanding blockchain might sound complicated, but it’s actually simpler than you think. This technology is not just a buzzword—it’s a powerful tool that can protect your data, boost trust, and open new opportunities for you. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how blockchain works, why it matters to you, and how it could impact your daily life in ways you never expected.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions. It stores data in blocks. Each block links to the one before it, forming a chain. This makes the information very hard to change or delete.
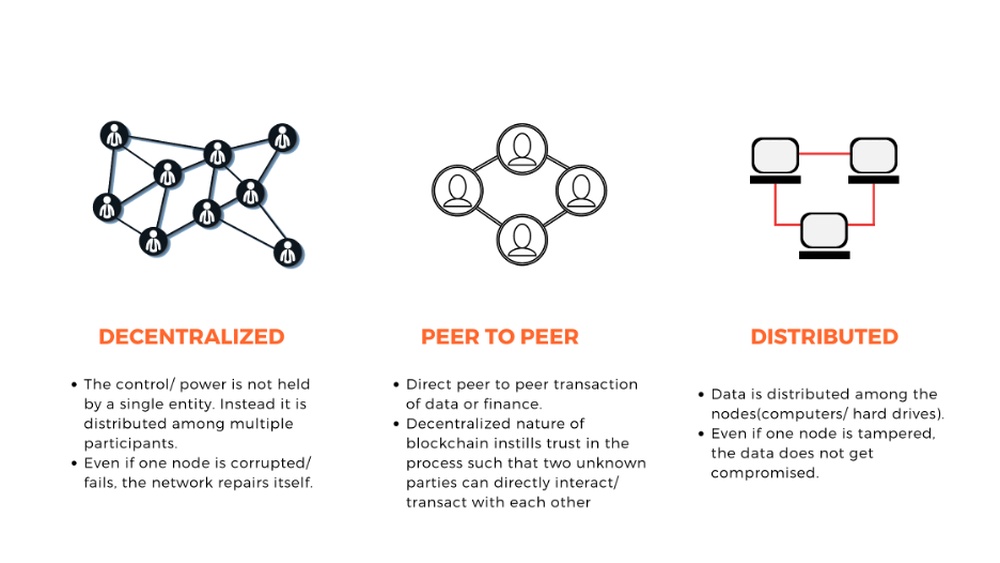
The system is decentralized. It means no single person or company controls it. Many computers, called nodes, work together to keep the blockchain safe and accurate.
When a new transaction happens, it is verified by these nodes. After verification, the transaction joins a block. The block is then added to the chain.
This process uses cryptography to keep data secure. Everyone can see the blockchain, but no one can easily change it. This makes blockchain transparent and trustworthy.
Key Features
Decentralization means no single person or group controls the data. Many computers share control, making it fair and open.
Immutability means once data is added, it cannot be changed or deleted. This keeps records safe and true forever.
Transparency allows anyone to see the transactions. This makes the system open and trustworthy.
Security uses strong math and computer codes to protect data. It stops hackers from breaking in or changing information.
Types Of Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to everyone. Anyone can join and see the transactions. They use decentralized networks to keep data safe and transparent. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples.
Private blockchains limit access to only certain people or groups. They are often used by companies to keep data private and control who can see or add information. These blockchains are faster but less open.
Consortium blockchains are run by a group of organizations. They share the control and decide who can join. This type is good for businesses that want to work together but keep some control over the data.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are programs that run on a blockchain. They work by following rules set in code. These contracts automatically perform tasks when conditions are met. No middleman needed. This makes transactions faster and cheaper.
Smart contracts help with many tasks. For example, they can manage financial agreements, track property ownership, or handle supply chains. They keep data secure and transparent. Everyone can see the contract’s status without changing it.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Automatic payments and loans without banks. |
| Real Estate | Secure transfer of property ownership records. |
| Supply Chain | Track products from start to end securely. |
| Insurance | Automatic claim approvals based on set rules. |
Applications Beyond Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology helps track goods in supply chains. It makes sure products are real and safe. Companies can see every step products take from factory to store.
In healthcare, blockchain keeps patient records safe and private. Doctors can share data quickly and without mistakes. It stops fake medicines from entering the market.
Finance uses blockchain for fast and safe money transfers. It cuts out middlemen, saving time and fees. Banks can check transactions easily and avoid fraud.
For voting systems, blockchain makes votes hard to change or fake. It helps count votes quickly and keeps results clear. People can trust that their vote is safe and private.

Credit: 101blockchains.com
Challenges And Limitations
Scalability is a big challenge for blockchain. Many blockchains can handle only a few transactions per second. This makes it hard to use for large-scale projects. The network can slow down or cost more when many people use it.
Energy Consumption is another issue. Some blockchains use a lot of electricity to work. This can harm the environment. It also makes running blockchain expensive for many users.
Regulatory Issues create uncertainty. Different countries have different rules about blockchain. Some rules are strict or unclear. This makes it hard for businesses to follow laws and use blockchain safely.
Future Innovations
Blockchain will work closely with AI to improve data security and decision-making. AI can help analyze blockchain data faster and smarter. The Internet of Things (IoT) will use blockchain to keep devices safe and connected. This means smart homes and cities become more reliable.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lets people handle money without banks. Blockchain makes transactions clear and safe. It can lower costs and speed up payments worldwide. Digital Identity on blockchain gives people control over their personal data. It helps prevent identity theft and fraud.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Blockchain_final-086b5b7b9ef74ecf9f20fe627dba1e34.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com

Credit: www.washingtontechnology.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Blockchain Technology And How Does It Work?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. It ensures data is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof by linking blocks of information using cryptography.
How Is Blockchain Different From Traditional Databases?
Unlike traditional databases, blockchain is decentralized and immutable. It does not rely on a central authority, making data more secure and resistant to fraud or unauthorized changes.
What Are The Main Benefits Of Using Blockchain?
Blockchain offers enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency. It reduces fraud, lowers transaction costs, and provides a trustworthy system for recording and verifying data.
Which Industries Use Blockchain Technology Today?
Blockchain is used in finance, supply chain, healthcare, real estate, and voting systems. It improves data transparency, traceability, and trust across various sectors.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology brings trust and security to digital transactions. It stores data in blocks linked together, making changes hard to do. Many industries use blockchain for transparency and safety. People can share information without a middleman. This technology keeps growing and changing how we handle data.
Understanding blockchain helps us see its future role. It offers a new way to protect and share information. The potential is clear, and the impact will expand soon.